|
Estradiol (Estrogen) is a female hormone, produced primarily in the
ovary. The amount of estrogen produced depends on the phase of the menstrual
cycle.
Men also produce estradiol, but only very small amounts.
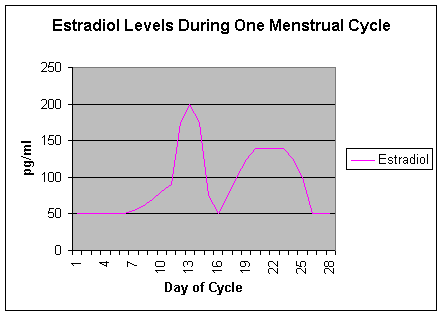
Shortly before ovulation, estradiol levels surge and then fall
immediately after ovulation. They then rise again and remain
elevated until 2-3 days before menstruation.
- If pregnancy occurs, the estradiol levels remain elevated.
- If pregnancy does not occur, then estradiol levels fall, which, in
combination with falling progesterone levels, provoke
a menstrual flow.
Elevations found in:
- Pregnancy
- Ovulation
- Second half of the menstrual cycle
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- Some hormone-producing tumors of the ovary
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCO, Stein-Levinthal Syndrome)
- Amenorrhea-Galactorrhea Syndrome
- Liver disease
Decreases found in:
- Menopause
- Pituitary failure
- Adrenal failure
- Ovarian failure
- Luteal Phase Deficiency
|
Normal Values*
| Men |
13-42 pg/ml |
|
Women
(Proliferative Phase) |
60-250 pg/ml |
Women
(Luteal Phase) |
75-450 pg/ml |
Women
(Menopausal) |
<10 pg/ml |
Women
(Menopausal on
estrogen
replacement) |
50-100 pg/ml |
*These are general values taken from a variety of
sources. The actual normal values may vary from lab to lab and from one
type of testing protocol to another.
|
