|
Fetal Presentation |
 |
|
|
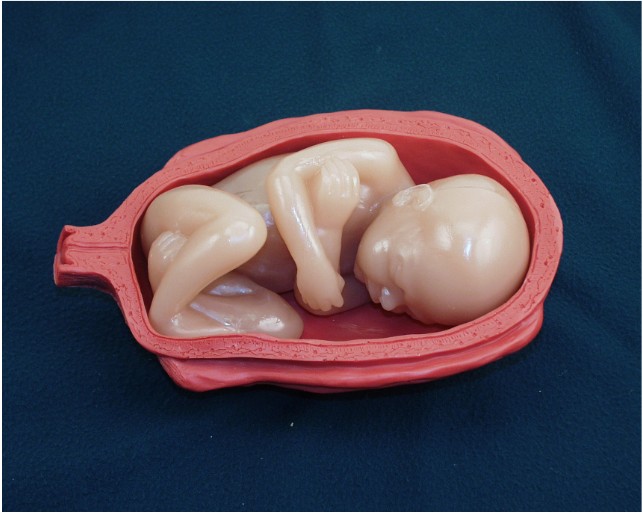 Fetal presentation means the
part of the fetus that is "presenting" at the cervix:
Fetal presentation means the
part of the fetus that is "presenting" at the cervix:
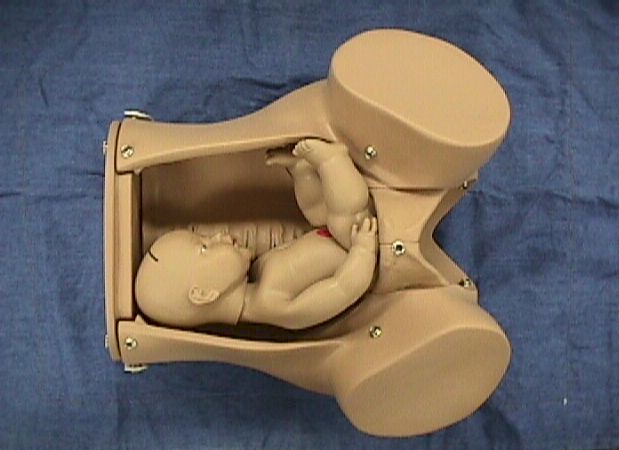
- Cephalic presentation means head first. This is the normal presentation.
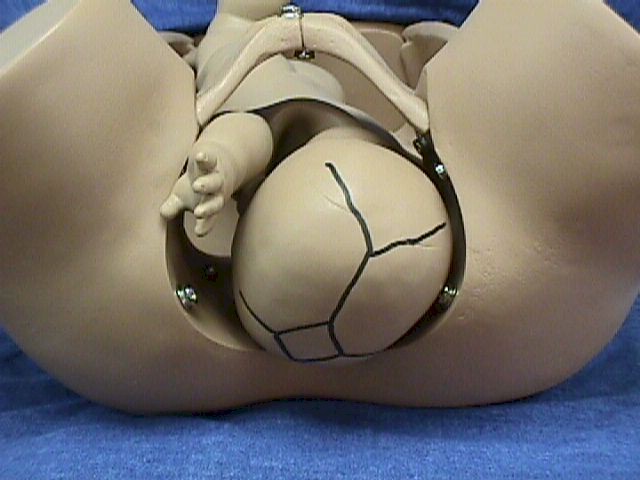
- Breech presentation means the fetal butt is coming out first.
- Transverse lie means the fetus is oriented from one side of the mother to the other and neither the head nor the butt is coming out first.
- Compound presentation means that a fetal hand is coming out with the fetal head.
- Shoulder presentation means that the fetal shoulder is trying to come out first.
Fetal "presentation" is different from fetal "position." Fetal position refers to the orientation of the fetus within the birth canal (eg, looking toward the mother's pubic bone (OP), or look toward the mother's coccyx (OA), etc.)
Read more about fetal position
Breech Presentation
Frank breech means the buttocks are presenting and the legs are up along the fetal
chest. The fetal feet are next to the fetal face. This is the safest
arrangement for breech delivery.
Footling breech means either one foot ("Single Footling") or both feet ("Double Footling") is presenting. This is also known as an incomplete breech.
Complete breech means the fetal thighs are flexed along the fetal abdomen, but the fetal shins and feet are tucked under the legs. The buttocks is presenting first, but the feet are very close. Sometimes during labor, a complete breech will shift to an incomplete breech if one or both of the feet extend below the fetal buttocks.
While many breech fetuses deliver vaginally without incident, this presentation is associated with an increased risk of:
- Fetal mechanical injury (fractures, nerve damage, and soft tissue injuries)
- Fetal asphyxia due to umbilical cord prolapse and obstruction, and fetal head entrapment.
For these reasons, many breech babies are delivered by cesarean section, and some obstetricians feel that all breech babies should be delivered in this way.
Read more about management of breech deliveries
Transverse Lie
If the fetus remains in a transverse lie, it cannot deliver deliver
vaginally as the diameter of the fetal presenting part (the whole body,
in this case) cannot descend through the birth canal.
If labor is allowed to continue for enough time with the fetus in transverse lie, the uterus will rupture. Even before the uterus ruptures, there is an increased risk in this presentation for prolapsed umbilical cord. For these reasons, women found to have a transverse lie in labor will usually have a cesarean section.
There are some exceptions to this indication for cesarean section:
- If labor is occurring during the middle trimester and fetus is not considered viable, it may be possible for this very small and fragile fetus to compress enough to squeeze through the pelvis. In this case, fetal survival would not be an issue.
- It may be possible to perform an external version, during which you manipulate the fetus, converting it to either breech or cephalic presentation. This is often more difficult than it sounds, particularly during labor, and carries some risk of injury to the fetus, placenta, umbilical cord, or uterus.
- In the case of twins, it would be acceptable to allow labor, even though the second twin is in transverse lie, anticipating that after delivery of the first twin, you would reach in and perform an internal version, converting the transverse lie to cephalic or breech presentation prior to delivery.
Some predisposing factors for a transverse lie include:
- Grand multiparity - more than 5 term pregnancies.
- Placenta previa
- Bony abnormalities of the pelvis
- Pelvic kidney
- Other pelvic mass
Transverse lie occurs frequently in early pregnancy, when it is of no consequence. At 16 weeks gestation, about half of all pregnancies will be transverse lie. This number steadily falls as pregnancy advances and the incidence of transverse lie by the 28th week is well below 10%. It falls steadily thereafter.
Whenever a fetal transverse lie is encountered near term or in labor, evaluate the patient carefully with ultrasound to determine if there are any predisposing factors, such as a placenta previa or pelvic kidney that could modify your management of the patient. So long as a placenta previa is not present, many obstetricians will check the patient's cervix at frequent intervals to detect early cervical dilatation and the consequential increased risk of cord prolapse. Sometimes, these patients are delivered early by scheduled cesarean section to avoid that risk.
|
|
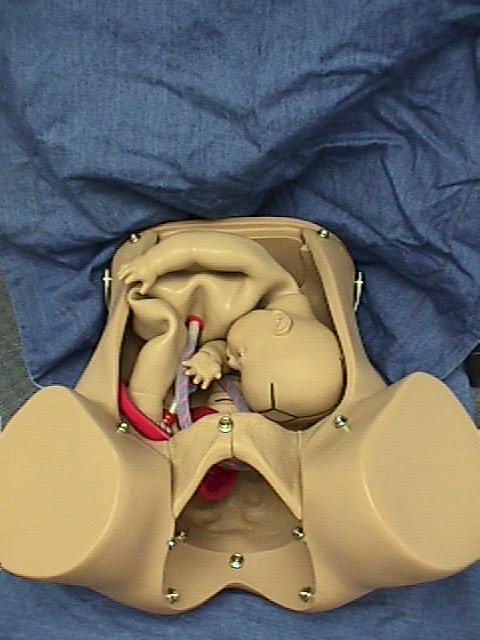
Compound Presentation
Compound presentation means that a fetal hand is coming out with the
fetal head. This is a problem because:
- The amount of baby that must come through the birth canal at one time is increased.
- There is increased risk of mechanical injury to the arm and shoulder, including fractures, nerve injuries and soft tissue injury.
A compound presentation may be resolvable if the fetus can be encouraged to withdraw the hand, for example.
If the fetus and arm are relatively small in comparison to the maternal pelvis, vaginal delivery may still be possible, but with some risk of injury to the arm.
If the fetus and arm are relatively large in comparison to the maternal pelvis, obstructed labor will occur and a cesarean will be needed.
Shoulder presentation
Shoulder presentation means that the fetal shoulder is trying to come
out first. This is a more advanced form of transverse lie and is
undeliverable vaginally.