 |
Mechanism of Normal Labor
There are five classical steps in the normal mechanism of labor. They
are:
- Descent
- Flexion
- Internal Rotation
- Extension
- External Rotation
Usually, labor progresses in this fashion, if the fetus is of average
size, with a normally positioned head, in a normal labor pattern in a
woman whose pelvis is of average size and gynecoid in shape.
There is overlap of these mechanisms. The fetal head, for example,
may continue to flex or increase its flexion while it is also internally
rotating and descending. |
 |
 |
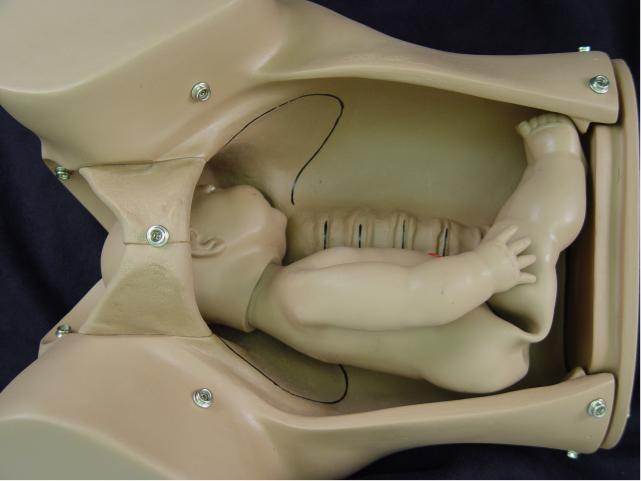
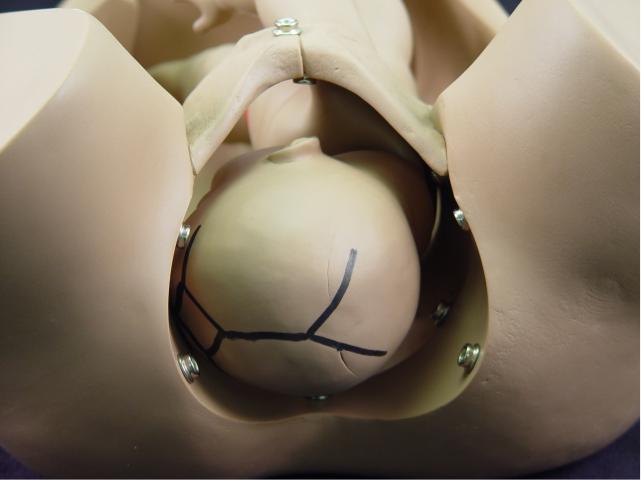
Descent: As the fetal head engages
and descends, it assumes an occiput transverse position because that is
the widest pelvic diameter available for the widest part of the fetal
head. |
 |
 |
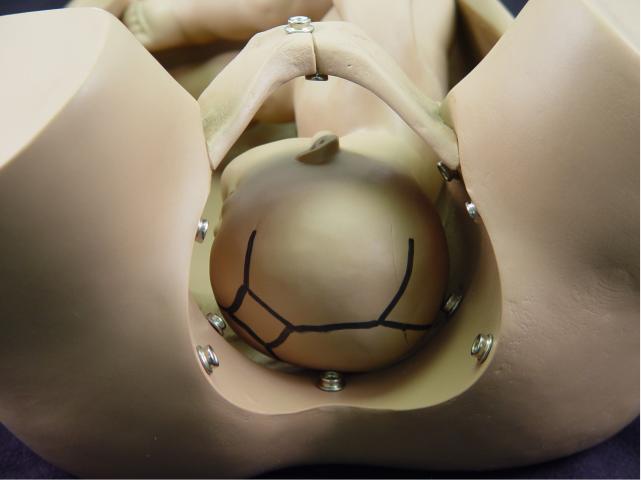
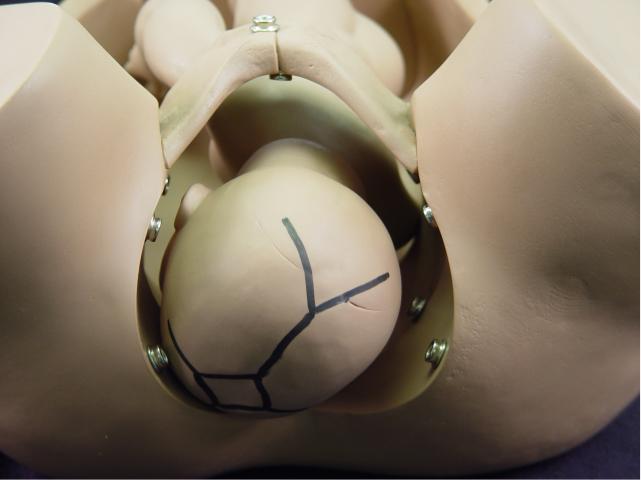
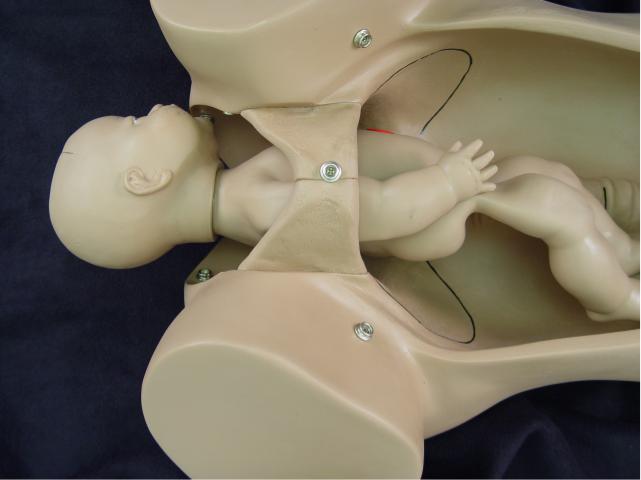
Flexion: While descending through
the pelvis, the fetal head flexes so that the fetal chin is touching the
fetal chest. This functionally creates a smaller structure to pass
through the maternal pelvis. When flexion occurs, the occipital
(posterior) fontanel slides into the center of the birth canal and the
anterior fontanel becomes more remote and difficult to feel. The fetal
position remains occiput transverse. |
 |
 |
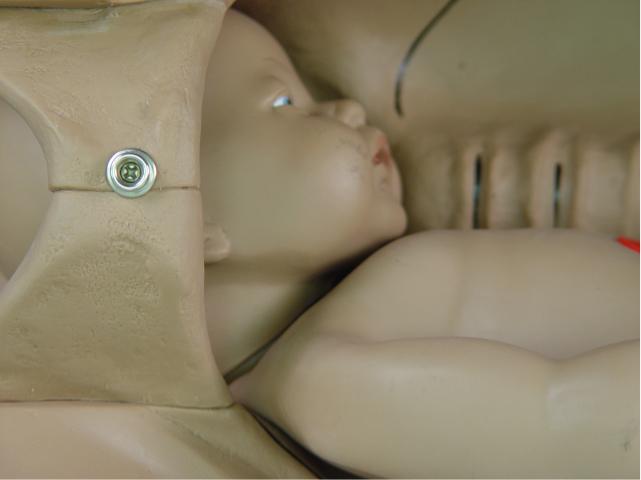
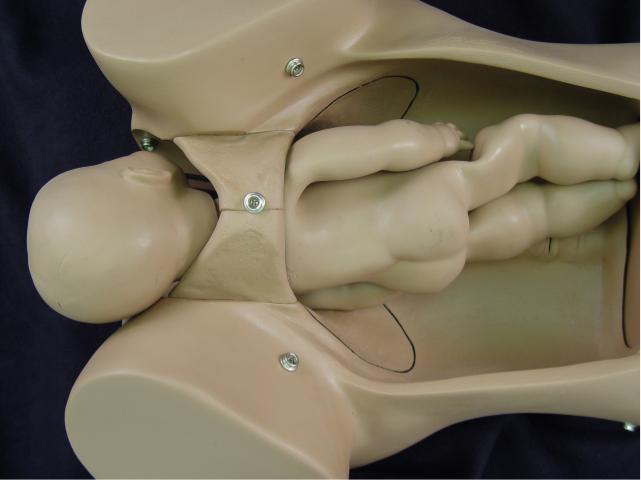
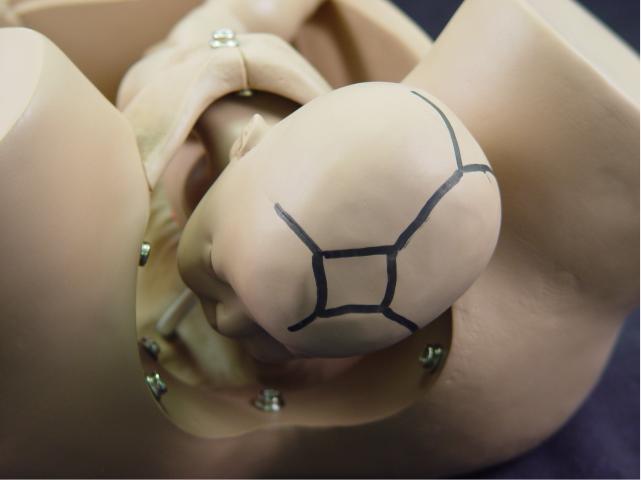
Internal Rotation: With further
descent, the occiput rotates anteriorly and the fetal head assumes an
oblique orientation. In some cases, the head may rotate completely to
the occiput anterior position. |
 |
 |
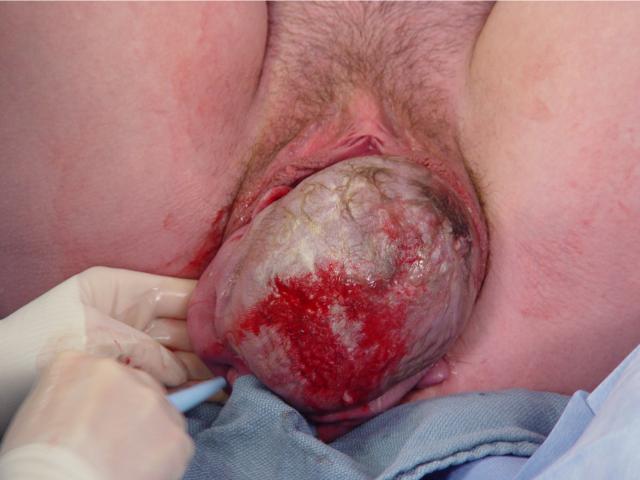
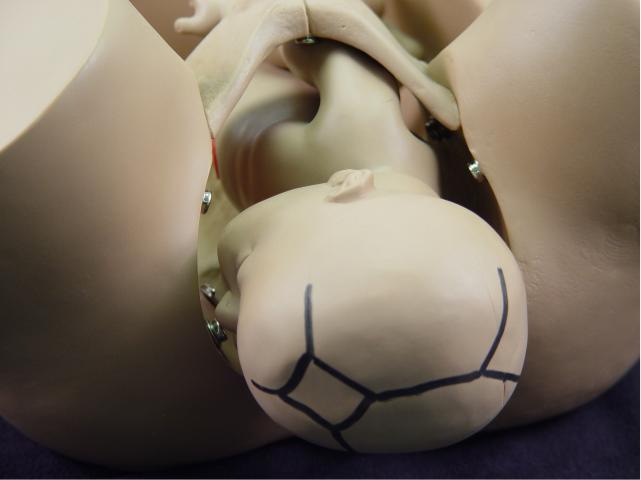
Extension: The curve of the hollow
of the sacrum favors extension of the fetal head as further descent
occurs. This means that the fetal chin is no longer touching the fetal
chest. |
 |
 |
External Rotation:
The shoulders rotate into an oblique or frankly anterior-posterior
orientation with further descent. This encourages the fetal head to
return to its transverse position. This is also known as restitution. |