|
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease |
 Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) represents a spectrum of
proliferative trophoblastic abnormalities. These abnormalities include
the hydatidiform mole (complete and incomplete), and gestational
trophoblastic tumors (metastatic and nonmetastatic).
Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) represents a spectrum of
proliferative trophoblastic abnormalities. These abnormalities include
the hydatidiform mole (complete and incomplete), and gestational
trophoblastic tumors (metastatic and nonmetastatic).
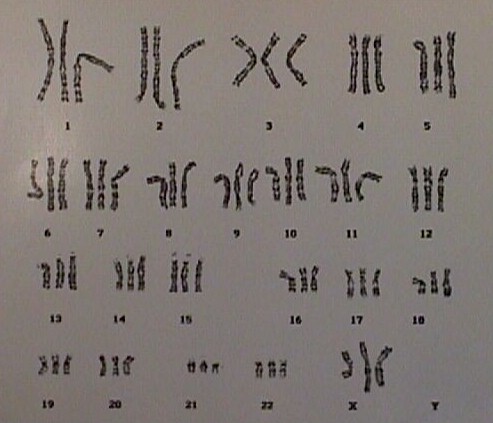
 Normal 46XX female karyotype
|
Hydatidiform
Mole
In the classical case of hydatidiform mole:
- A fetus and amnion never form
- There is hydropic swelling of the chorionic villous stroma, and absence of blood vessels within these villi.
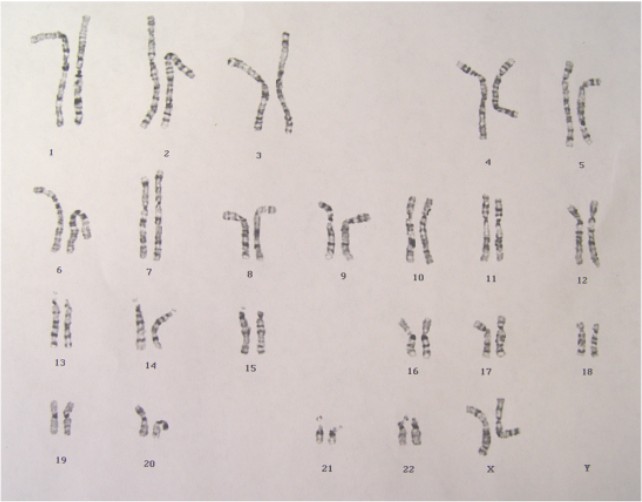
- Most (85%) of the chromosomes are 46XX, but of totally paternal origin
- Varying degrees of trophoblastic epithelial proliferation
- Patients present with bleeding in the first (or early 2nd) trimester, sometimes profusely.
- Ultrasound scans show absence of a fetus and a "Swiss Cheese" appearance within the placenta
- Any tissue that is passed or removed has a resemblance to a cluster of grapes
Pregnancies complicated by GTD produce larger than usual amounts of HCG. Women with GTD tend to have more trouble with nausea and the incidence of early but severe pre-eclampsia is relatively high.
Following D&C, 80% of patients are cured and there is no recurrence of this molar pregnancy. In about 20%, however, a trophoblastic tumor developed. Most of the tumors were invasive mole and a few of them were choriocarcinoma.
Treatment
- Chest x-ray to rule out pulmonary metastases
- D&C
- Serial Quantitative HCG levels every 2 weeks until HCG falls to normal levels
- Then monthly HCG levels for 1 year, watching for recurrence
- No pregnancy for 1 year
- If any significant rise in HCG during the year of observation, methotrexate therapy
- Hysterectomy is acceptable therapy if no further childbearing is desired.
Partial Mole
In the case of a partial mole, a fetus, amnion and fetal circulation are
usually present. Triploidy (69,XXX or 69, XXY, with one maternal and two
paternal haploid complements) is typically found.
Choriocarcinoma
The most dangerous form of GTD. If untreated, it is often swiftly fatal,
with distant metastases in the lungs, liver and brain. Most cases are
sensitive to methotrexate, however, and cures are common if aggressively
treated early in the course of the disease.