|
Diagnosis of Pregnancy |
 Pregnancy may be suspected in any sexually active woman, of childbearing
age, whose menstrual period is delayed, particularly if combined with
symptoms of early pregnancy, such as:
Pregnancy may be suspected in any sexually active woman, of childbearing
age, whose menstrual period is delayed, particularly if combined with
symptoms of early pregnancy, such as:
- Nausea (1st trimester)
- Breast and nipple tenderness (1st trimester)
- Marked fatigue (1st and 3rd trimesters)
- Urinary frequency (1st and 3rd trimesters)
- The patient thinks she's pregnant
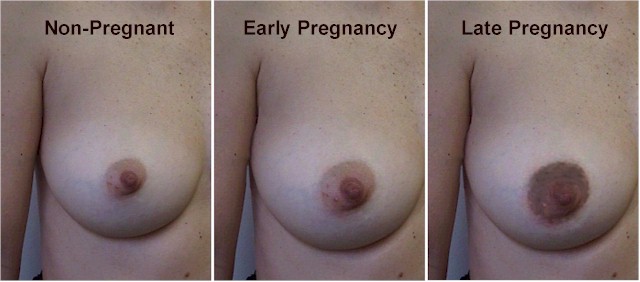 Early signs of pregnancy may include:
Early signs of pregnancy may include:
- Blue discoloration of the cervix and vagina (Chadwick's sign)
- Softening of the cervix (Goodell's sign)
- Softening of the uterus (Ladin's sign and Hegar's sign)
- Darkening of the nipples
- Unexplained pelvic or abdominal mass
Pregnancy should be confirmed with a reliable pregnancy test. Urine or serum pregnancy tests can be used. Both are reliable and detect human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG). Pregnancy is considered present if 30-35 mIU of HCG are present in the urine or serum.
Ultrasound may be used to confirm a pregnancy, if the gestational age is old enough for visualization of a recognizable fetus and fetal heartbeat. In that situation, a confirmatory HCG is not necessary.