
 |
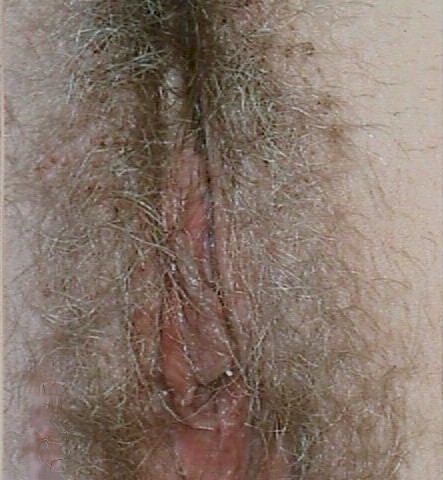
 Pubic lice (pediculosis pubis) is caused by the infestation of the pubic
hair and skin by tiny organisms that are just at the limits of visibility without
magnification. Pubic lice (pediculosis pubis) is caused by the infestation of the pubic
hair and skin by tiny organisms that are just at the limits of visibility without
magnification.Pubic lice can be spread through sexual contact, close living quarters, or shared
clothing.
The patient will described moderately intense itching and may say, "I think I see
something moving down there."
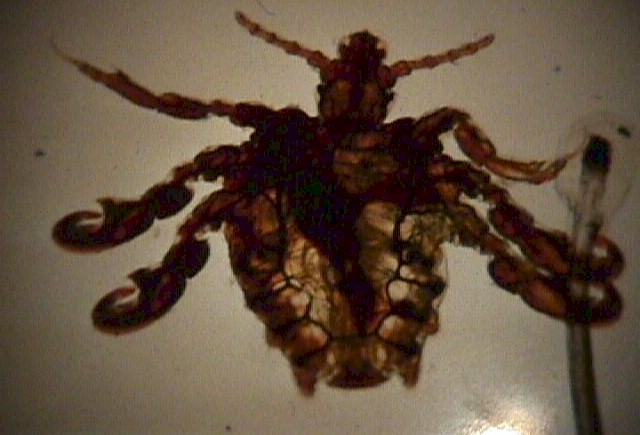
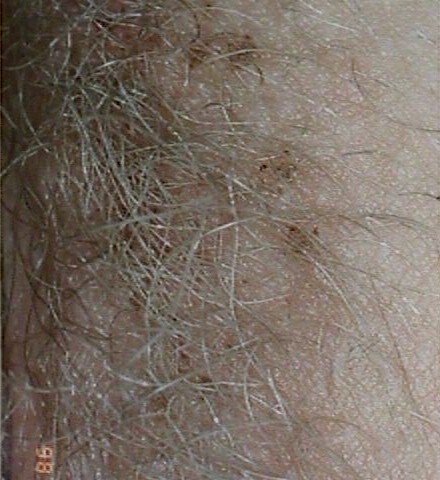
Ideally, the patient is examined with good lighting and a magnifying lens. The lice can
be seen moving along the shafts of the pubic hair. Individual "nits" can be
seen. These are small, oval, gray eggs attached to the hairs. Brown discolorations of the
skin, when closely examined, are seen to contain lice excrement deposited just beneath the
skin.
Without magnification, the brown spots can be seen, but most noticeable is the movement
of the lice.
Treatment may include:
- Nix cream (5% permethrin) applied to the vulvar skin and left in place for 6-12 hours
before washing off.
- Kwell lotion or shampoo (1% lindane) once after showering and left in place for 10
minutes before rinsing. This may be repeated in 7 days if necessary. Do not use more often
or longer than this as lindane has neurotoxicity potential.
- Mechanically removing nits and lice by combing the pubic hair with a fine toothed comb.
- Clothing and bed linens should be thoroughly washed and dried. Mattresses should be
aired or vacuumed. Sources of cross-contamination (shared clothing, towels) eliminated.
Sexual contacts should be treated.
If conventional medication is not available, petroleum jelly, applied to the affected
area may prove effective by suffocating the lice.
|